rolling_filter#
- movement.filtering.rolling_filter(data, window, statistic='median', min_periods=None, print_report=False)[source]#
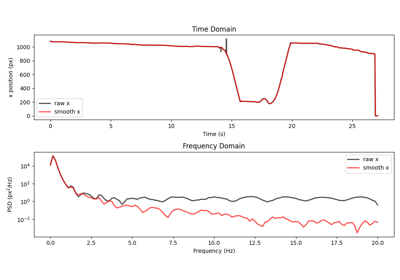
Apply a rolling window filter across time.
This function uses
xarray.DataArray.rolling()to apply a rolling window filter across thetimedimension of the input data and computes the specifiedstatisticover each window.- Parameters:
data (xarray.DataArray) – The input data array.
window (int) – The size of the rolling window, representing the fixed number of observations used for each window.
statistic (str) – Which statistic to compute over the rolling window. Options are
median,mean,max, andmin. The default ismedian.min_periods (int) – Minimum number of observations in the window required to have a value (otherwise result is NaN). The default, None, is equivalent to setting
min_periodsequal to the size of the window. This argument is directly passed to themin_periodsparameter ofxarray.DataArray.rolling().print_report (bool) – Whether to print a report on the number of NaNs in the dataset before and after smoothing. Default is
False.
- Returns:
The filtered data array.
- Return type:
Notes
By default, whenever one or more NaNs are present in the window, a NaN is returned to the output array. As a result, any stretch of NaNs present in the input data will be propagated proportionally to the size of the window (specifically, by
floor(window/2)). To control this behaviour, themin_periodsoption can be used to specify the minimum number of non-NaN values required in the window to compute a result. For example, settingmin_periods=1will result in the filter returning NaNs only when all values in the window are NaN, since 1 non-NaN value is sufficient to compute the result.